Why command-line proficiency accelerates AI development and enables powerful data processing pipelines
Terminal Mastery for AI Engineers: Essential Skills for Production Systems

Why command-line proficiency accelerates AI development and enables powerful data processing pipelines
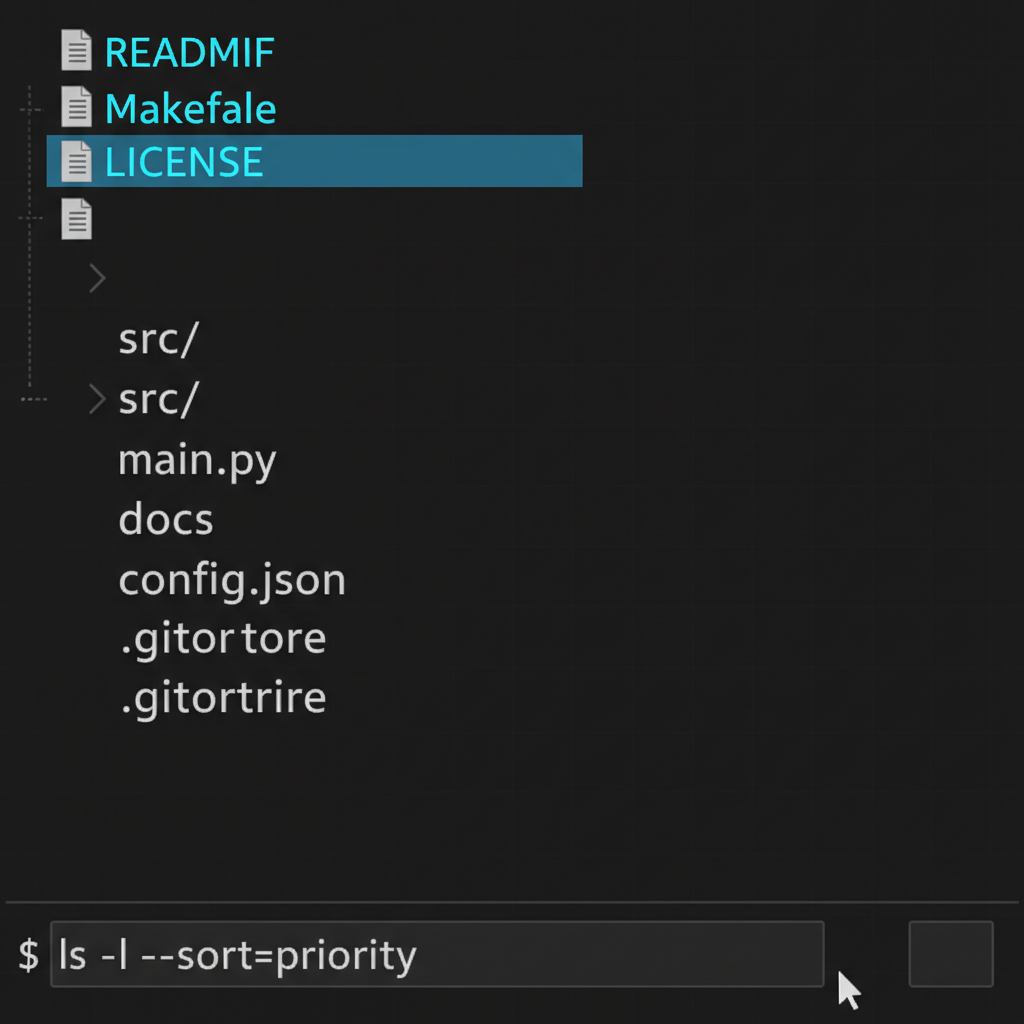
In production AI systems processing millions of files daily, naming conventions aren’t trivial details - they’re critical infrastructure decisions. A recent incident where a junior engineer renamed all uppercase files to lowercase caused our data pipeline to miss critical configuration files for three hours. This highlighted why understanding and respecting established conventions matters.
Traditional Unix systems established uppercase filenames for important files - README, Makefile, LICENSE. This wasn’t arbitrary; it leveraged the ASCII sorting order where uppercase letters precede lowercase, creating natural visual hierarchy in terminal listings.
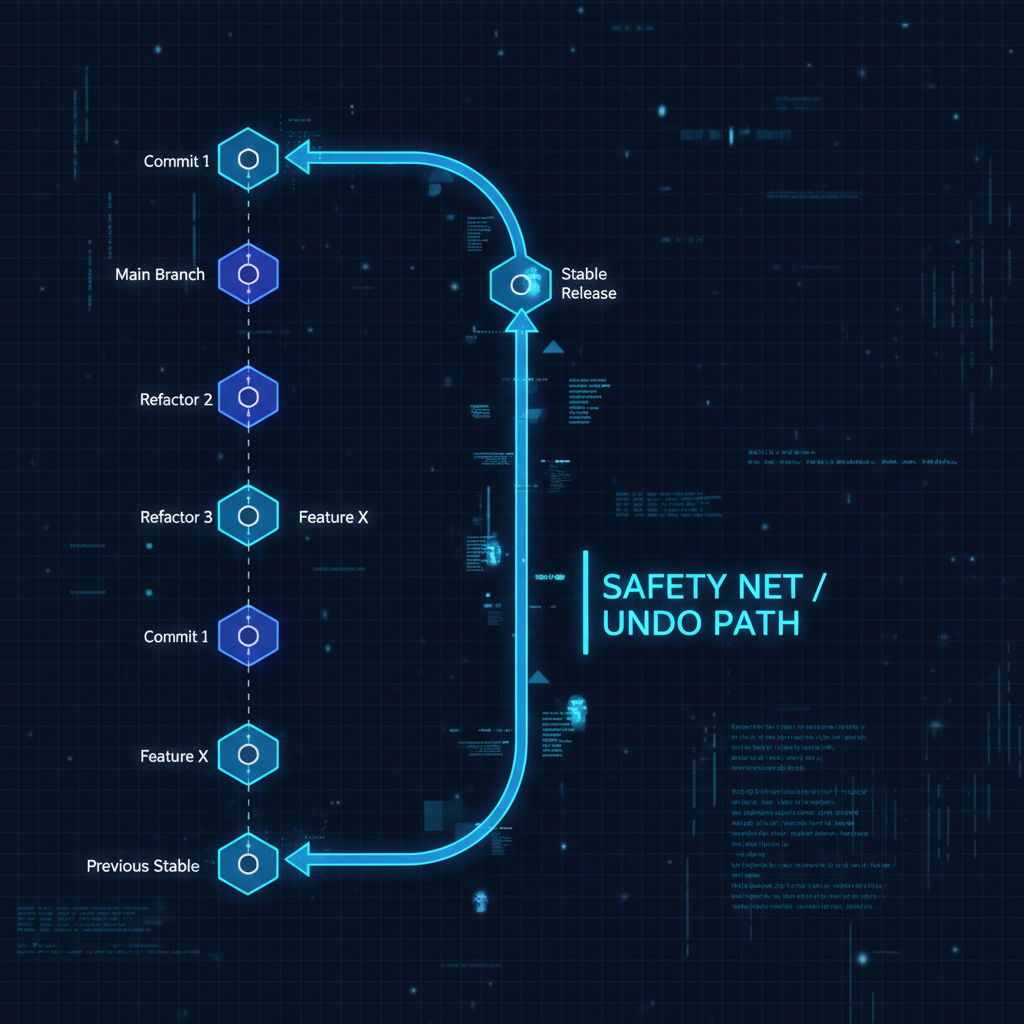
Developers often hesitate to experiment with Git operations because they fear irreversible mistakes. This hesitation slows down development and prevents teams from fully leveraging Git’s capabilities. The solution isn’t to be more careful—it’s to understand and use git reflog as a fundamental safety mechanism.
git reflog maintains a local history of every reference update in your repository. This includes commits, checkouts, resets, and rebases—essentially every action that moves HEAD or updates branch pointers. This reference log acts as a recovery mechanism, allowing you to restore your repository to any previous state within the reflog’s retention window (typically 90 days for reachable commits).
Building production AI systems requires intense focus. Every new feature, every experiment, every optimization competes for limited resources - engineer time, GPU hours, and cognitive bandwidth. The teams that ship successful products aren’t those that do everything; they’re those that master the discipline of not doing.
Consider a typical AI team’s potential workload:
class ProjectLoad:
def __init__(self):
self.potential_projects = [
"Implement transformer architecture",
"Build real-time inference pipeline",
"Create data labeling platform",
"Optimize model for edge deployment",
"Develop explainability dashboard",
"Refactor feature engineering pipeline",
"Implement A/B testing framework",
"Build model monitoring system",
"Create automated retraining pipeline",
"Develop custom loss functions"
]
def calculate_completion_rate(self, projects_attempted):
capacity = 100 # Team capacity units
effort_per_project = 30 # Average effort units
context_switching_cost = 5 * (projects_attempted - 1)
actual_capacity = capacity - context_switching_cost
completion_rate = min(1.0, actual_capacity / (projects_attempted * effort_per_project))
return {
'projects_attempted': projects_attempted,
'completion_rate': completion_rate,
'projects_completed': int(projects_attempted * completion_rate)
}
# Results:
# 2 projects: 95% completion = 2 completed
# 5 projects: 60% completion = 3 completed
# 10 projects: 20% completion = 2 completed
Attempting everything guarantees completing nothing of value.
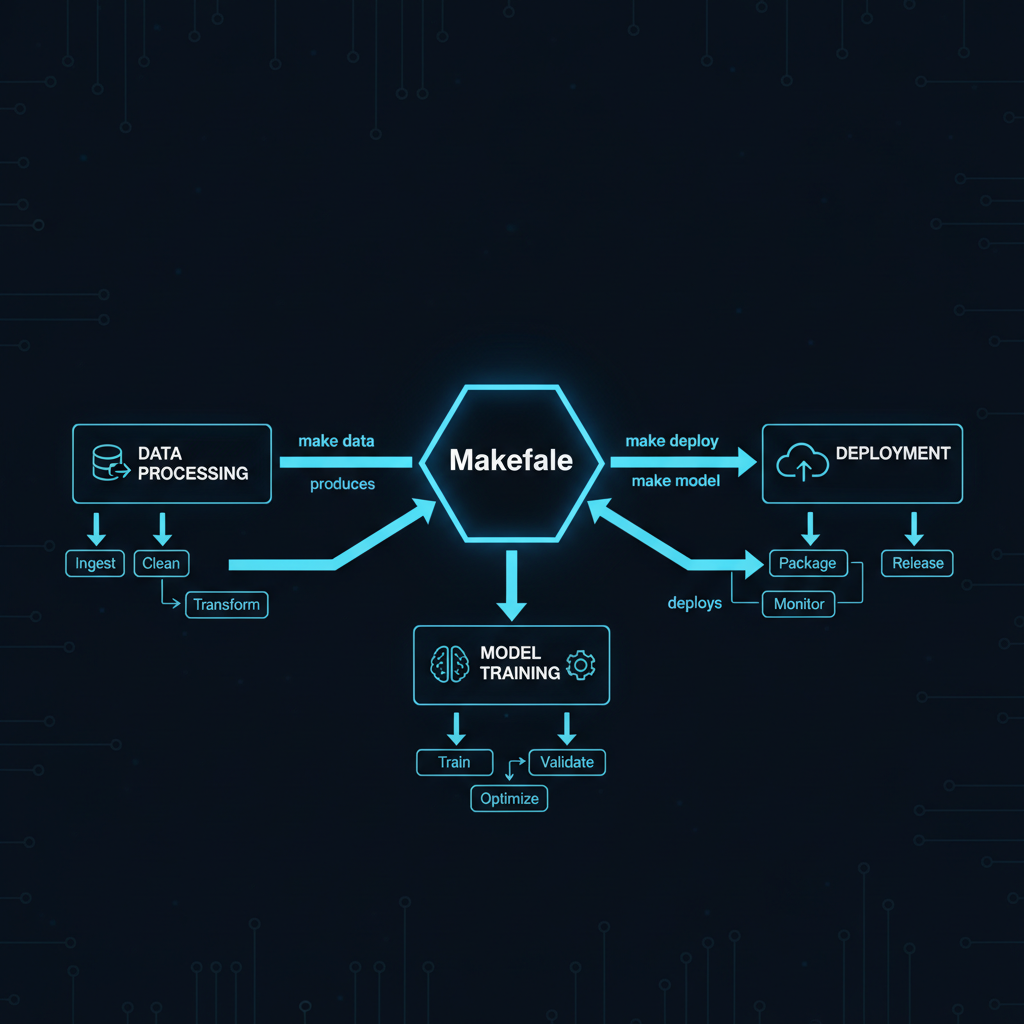
In the era of complex ML pipelines, where data processing, model training, and deployment involve dozens of interdependent steps, Makefiles provide a battle-tested solution for orchestration. While newer tools promise simplicity through abstraction, Makefiles offer transparency, portability, and power that modern AI systems demand.
Modern ML projects involve intricate dependency chains:
Makefiles handle these challenges elegantly through their fundamental design: declarative dependency management with intelligent rebuild detection.