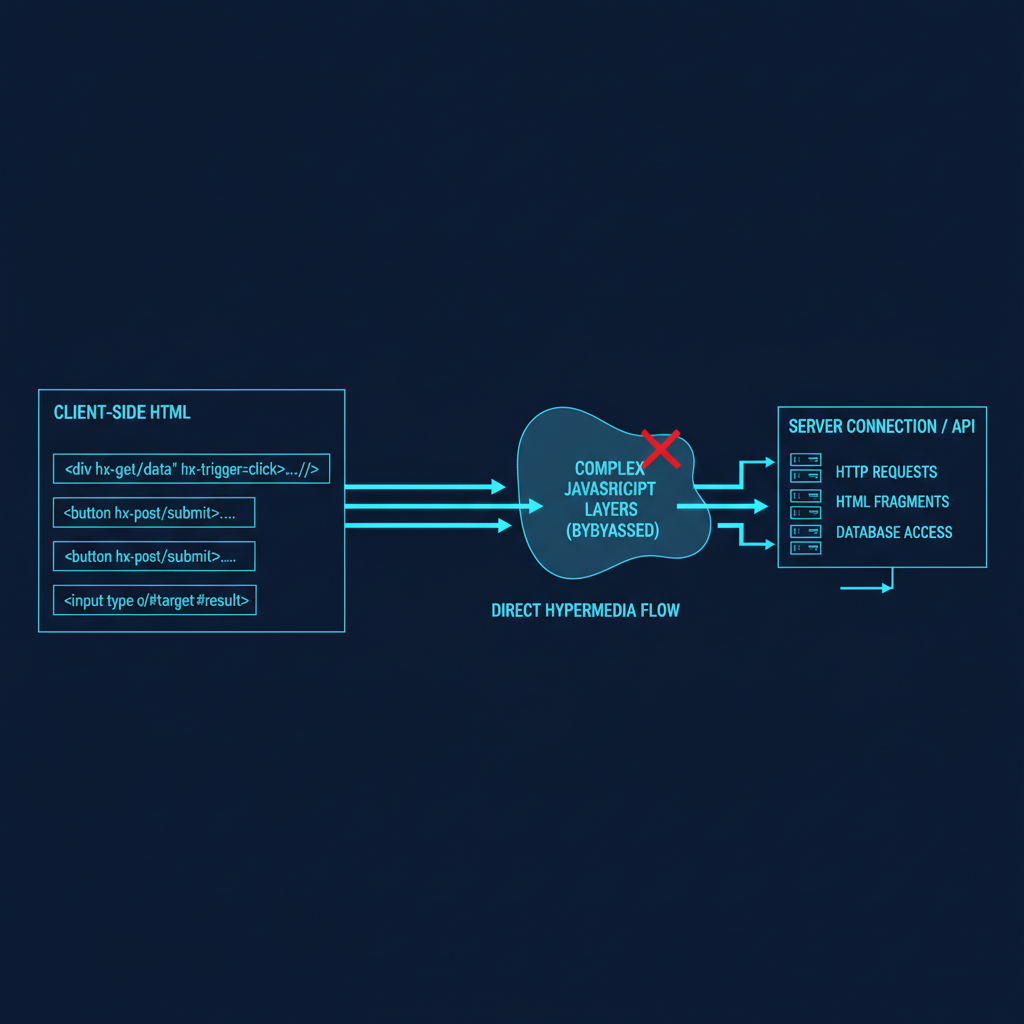
Modern AI applications demand responsive, real-time interfaces that can handle everything from streaming model outputs to live feature updates. HTMX offers a pragmatic approach to building these interfaces without the complexity of full JavaScript frameworks - particularly valuable when your team’s expertise lies in ML engineering rather than frontend development.
The Challenge: AI UIs Without Frontend Complexity
Building interfaces for AI systems presents unique challenges:
- Streaming responses from large language models
- Real-time visualization of training metrics
- Dynamic form updates based on model predictions
- Live collaboration on annotation tasks
- Progressive disclosure of complex model outputs
Traditional approaches require substantial JavaScript expertise. HTMX changes this equation by extending HTML’s capabilities directly.