HTMX for AI Interfaces: Simplicity That Scales
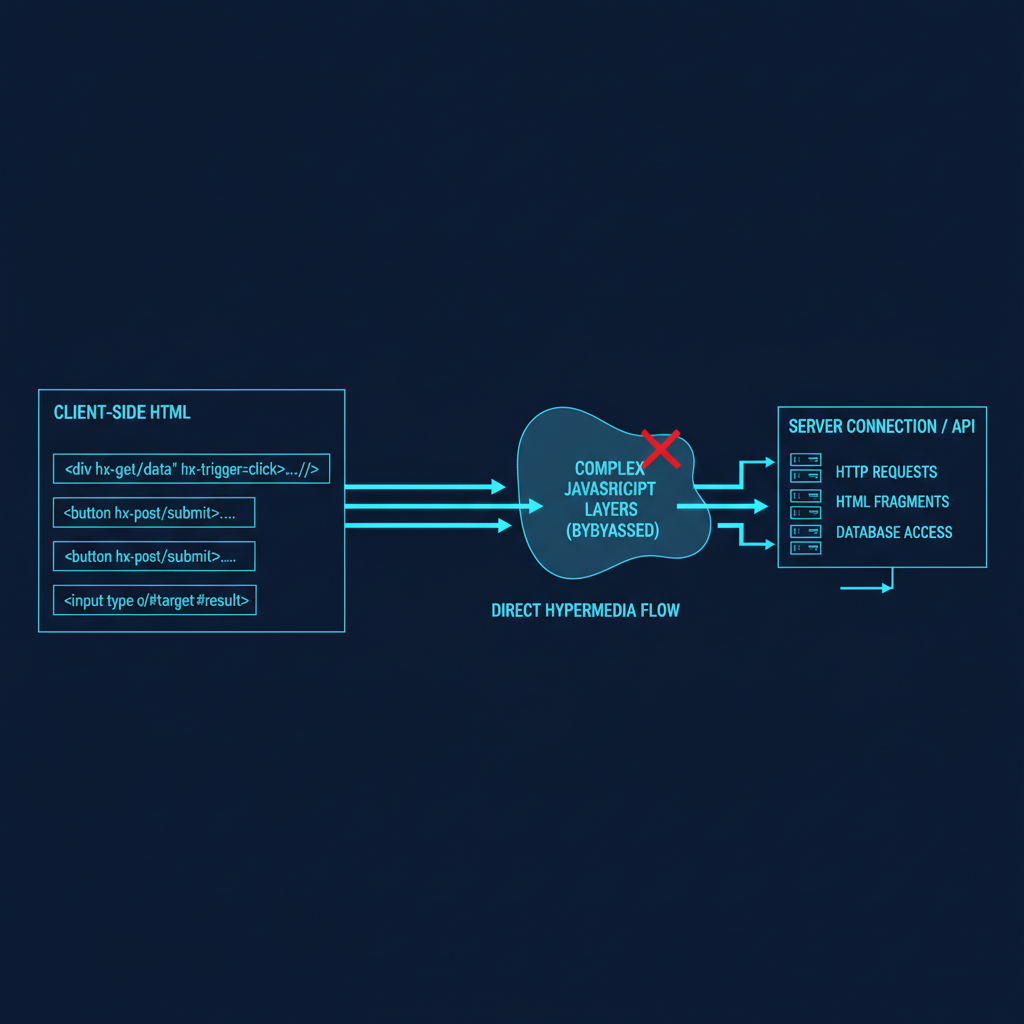
Modern AI applications demand responsive, real-time interfaces that can handle everything from streaming model outputs to live feature updates. HTMX offers a pragmatic approach to building these interfaces without the complexity of full JavaScript frameworks - particularly valuable when your team’s expertise lies in ML engineering rather than frontend development.
The Challenge: AI UIs Without Frontend Complexity#
Building interfaces for AI systems presents unique challenges:
- Streaming responses from large language models
- Real-time visualization of training metrics
- Dynamic form updates based on model predictions
- Live collaboration on annotation tasks
- Progressive disclosure of complex model outputs
Traditional approaches require substantial JavaScript expertise. HTMX changes this equation by extending HTML’s capabilities directly.
Getting Started: One Line to Transform Your Stack#
<script src="https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.10"></script>
That single line unlocks capabilities that traditionally require thousands of lines of JavaScript. For AI applications, this means your ML engineers can build sophisticated interfaces without context-switching to frontend frameworks.
Real-World AI Application Patterns#
1. Streaming LLM Responses#
Instead of complex WebSocket handling in JavaScript, HTMX makes streaming straightforward:
<div hx-ws="connect:/api/llm-stream">
<form hx-ws="send">
<input name="prompt" placeholder="Enter your prompt...">
<button>Generate</button>
</form>
<div id="response" hx-swap="beforeend">
<!-- Streaming tokens appear here -->
</div>
</div>
On the backend (Python/FastAPI example):
@app.websocket("/api/llm-stream")
async def llm_stream(websocket: WebSocket):
await websocket.accept()
while True:
data = await websocket.receive_json()
prompt = data.get('prompt')
async for token in model.generate_stream(prompt):
await websocket.send_text(
f'<span class="token">{token}</span>'
)
2. Live Model Inference with Progressive Enhancement#
<form hx-post="/api/classify"
hx-target="#results"
hx-indicator="#spinner">
<input type="file" name="image" accept="image/*">
<button>Classify Image</button>
</form>
<div id="spinner" class="htmx-indicator">
Processing with ResNet-50...
</div>
<div id="results"></div>
The server returns progressive results as HTML:
@app.post("/api/classify")
async def classify(image: UploadFile):
# Quick initial prediction
initial = await quick_model.predict(image)
yield f'<div class="initial">Quick result: {initial}</div>'
# Detailed analysis
detailed = await detailed_model.predict(image)
yield f'<div class="detailed">Confidence scores: {detailed}</div>'
# Explanation
explanation = await explainer.explain(image, detailed)
yield f'<div class="explanation">{explanation}</div>'
3. Real-time Training Metrics Dashboard#
<div hx-get="/api/training/metrics"
hx-trigger="every 2s"
hx-swap="innerHTML">
<!-- Metrics update automatically -->
</div>
<!-- Interactive parameter adjustment -->
<input type="range"
name="learning_rate"
hx-post="/api/training/adjust"
hx-trigger="change"
hx-target="#confirmation"
min="0.0001" max="0.1" step="0.0001">
4. Collaborative Annotation Interface#
<div class="annotation-task">
<img src="/api/image/{{task_id}}">
<div class="annotations"
hx-get="/api/annotations/{{task_id}}"
hx-trigger="sse:annotation-updated">
<!-- Live updates when other users annotate -->
</div>
<button hx-post="/api/annotate"
hx-vals='{"task_id": "{{task_id}}", "label": "positive"}'>
Mark Positive
</button>
</div>
Advanced Patterns for Production AI Systems#
Server-Sent Events for Model Training#
<div hx-sse="connect:/api/training/events">
<div hx-sse="swap:epoch">
<!-- Updates on each epoch -->
</div>
<div hx-sse="swap:metrics">
<!-- Live metrics -->
</div>
<div hx-sse="swap:checkpoint">
<!-- Checkpoint notifications -->
</div>
</div>
Intelligent Form Validation#
<input name="email"
hx-post="/api/validate/email"
hx-trigger="blur changed delay:500ms"
hx-target="#email-error">
<input name="api_key"
hx-post="/api/validate/api-key"
hx-trigger="blur"
hx-target="#key-status">
Dynamic Model Selection#
<select name="model_type"
hx-get="/api/model/options"
hx-target="#model_specific_options"
hx-trigger="change">
<option value="transformer">Transformer</option>
<option value="cnn">CNN</option>
<option value="rnn">RNN</option>
</select>
<div id="model_specific_options">
<!-- Model-specific parameters load here -->
</div>
Performance Optimizations for AI Workloads#
1. Request Debouncing for Expensive Operations#
<!-- Only trigger inference after user stops typing -->
<input hx-post="/api/suggest"
hx-trigger="keyup changed delay:500ms"
hx-target="#suggestions">
2. Partial Page Updates for Large Results#
<!-- Load results in chunks -->
<div hx-get="/api/results?page=1"
hx-trigger="revealed"
hx-swap="afterend">
<!-- Infinite scroll for large datasets -->
</div>
3. Optimistic UI Updates#
<button hx-post="/api/train/start"
hx-swap="outerHTML"
hx-vals='{"immediate": "<div>Training started...</div>"}'>
Start Training
</button>
Integration with AI Infrastructure#
MLflow Integration#
<div hx-get="/api/mlflow/experiments"
hx-trigger="load"
hx-target="#experiments">
</div>
<script>
// Minimal JS for MLflow metric charts
htmx.on("htmx:afterSwap", function(evt) {
if (evt.target.id === "metrics-chart") {
renderMetricsChart(evt.detail.xhr.response);
}
});
</script>
Kubernetes Job Management#
<div class="job-controller">
<button hx-post="/api/k8s/job/start"
hx-confirm="Start distributed training job?">
Launch Training
</button>
<div hx-get="/api/k8s/job/status"
hx-trigger="every 5s">
<!-- Job status updates -->
</div>
</div>
Security Considerations for AI Applications#
CSRF Protection#
<meta name="htmx-config"
content='{"getCacheBusterParam": true,
"includeIndicatorStyles": false,
"historyCacheSize": 0}'>
<!-- Include CSRF token in all requests -->
<body hx-headers='{"X-CSRF-Token": "{{ csrf_token }}"}'>
API Key Management#
<!-- Never expose API keys in client code -->
<form hx-post="/api/proxy/openai"
hx-target="#response">
<!-- Server handles API authentication -->
</form>
Production Deployment Patterns#
CDN and Caching Strategy#
<!-- Version-locked for production stability -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/htmx.org@1.9.10/dist/htmx.min.js"
integrity="sha384-..."
crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
Progressive Enhancement#
<!-- Fallback for non-HTMX browsers -->
<form action="/api/process" method="POST"
hx-post="/api/process"
hx-target="#results">
<!-- Works with and without HTMX -->
</form>
Metrics and Monitoring#
Track HTMX performance in production:
htmx.on("htmx:beforeRequest", function(evt) {
// Log to monitoring service
monitor.startTimer(evt.detail.elt.id);
});
htmx.on("htmx:afterRequest", function(evt) {
monitor.endTimer(evt.detail.elt.id, {
status: evt.detail.xhr.status,
duration: evt.detail.elapsed
});
});
Team Adoption Strategy#
For ML teams adopting HTMX:
- Start with read-only dashboards - Minimal risk, maximum impact
- Add interactive elements gradually - Forms, filters, search
- Implement real-time features last - WebSockets, SSE
- Maintain progressive enhancement - Ensure fallbacks exist
Performance Benchmarks#
From production deployments:
- Initial page load: 40% faster than React equivalent
- Time to interactive: 200ms vs 2s for SPA
- Bundle size: 14KB vs 300KB+ for typical React app
- Developer velocity: 3x faster for ML engineers
Integration Benefits#
For teams building production AI systems, HTMX offers:
- Reduced complexity: Focus on AI logic, not frontend frameworks
- Better performance: Smaller payloads, faster interactions
- Server-rendered content: Better SEO by default
- Lower maintenance: Less JavaScript to debug and update
Within days, ML engineers can build interfaces that would traditionally require dedicated frontend developers. This accelerates AI product development and reduces the gap between model development and user value delivery.